Did you know that Swarthmore College has a JupyterHub installation that allows you to work on and save your Jupyter Notebooks in the cloud?
What is a Jupyter Notebook?
A Jupyter Notebook is a computing environment that enables the author to write content containing interactive code, videos, charts, and pretty much anything else the Jupyter kernel (In Swarthmore’s case, Python) provides.
What can I do with a Jupyter Notebook?
- Run and edit code in the browser
- See the results of computation through rich media representations such as HTML, PNG, SVG, PDF, etc.
- Create narrative text using Markdown
More about Jupyter Notebooks
A Jupyter Notebook is composed of blocks called cells. Each cell can have a different type. They will most commonly have a type of Markdown or Code. In the example below, the top cell is a Markdown cell while the bottom is Code cell.
Within your notebook, you can do things like import libraries, visualize data, and even share your created notebooks with others.
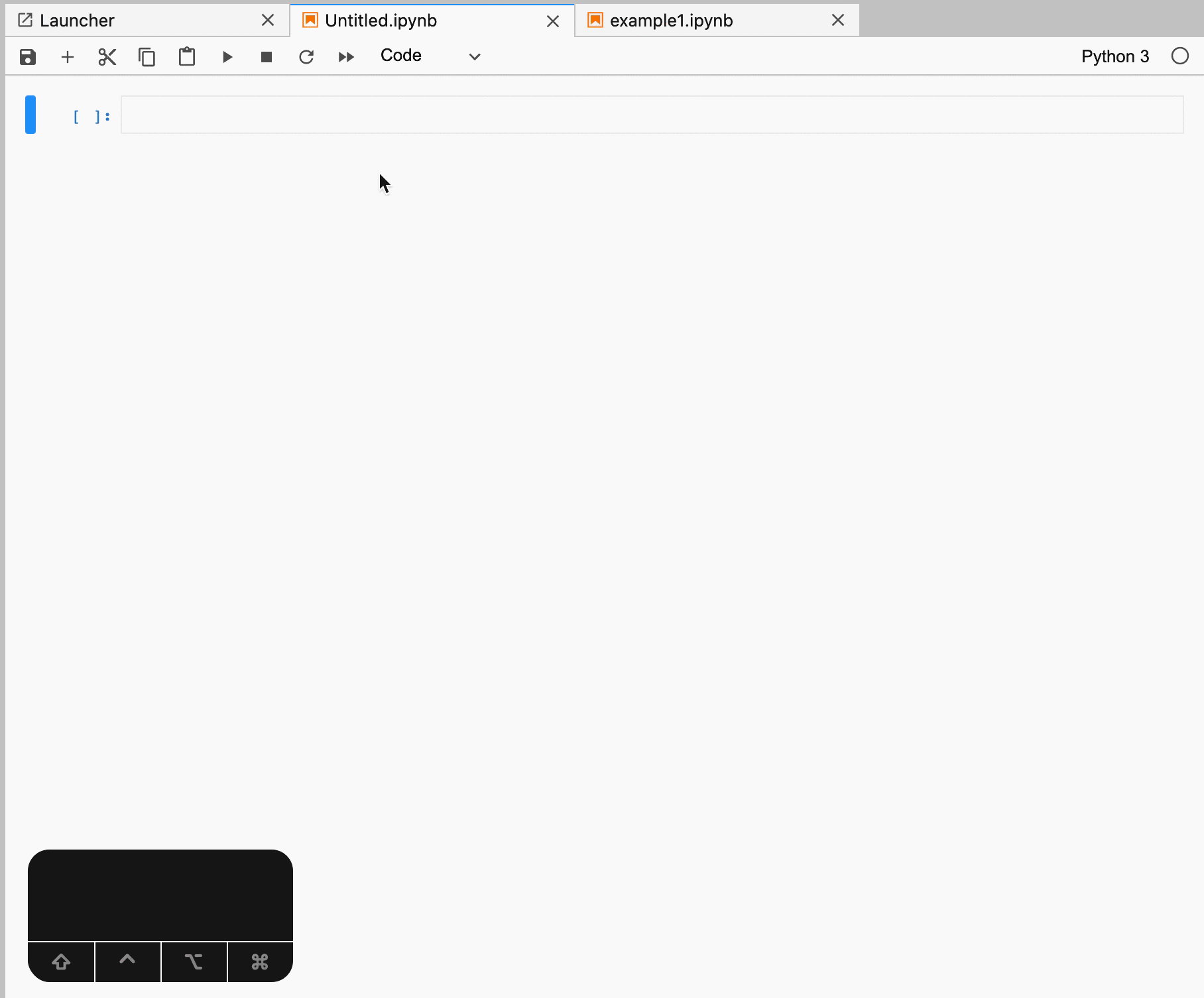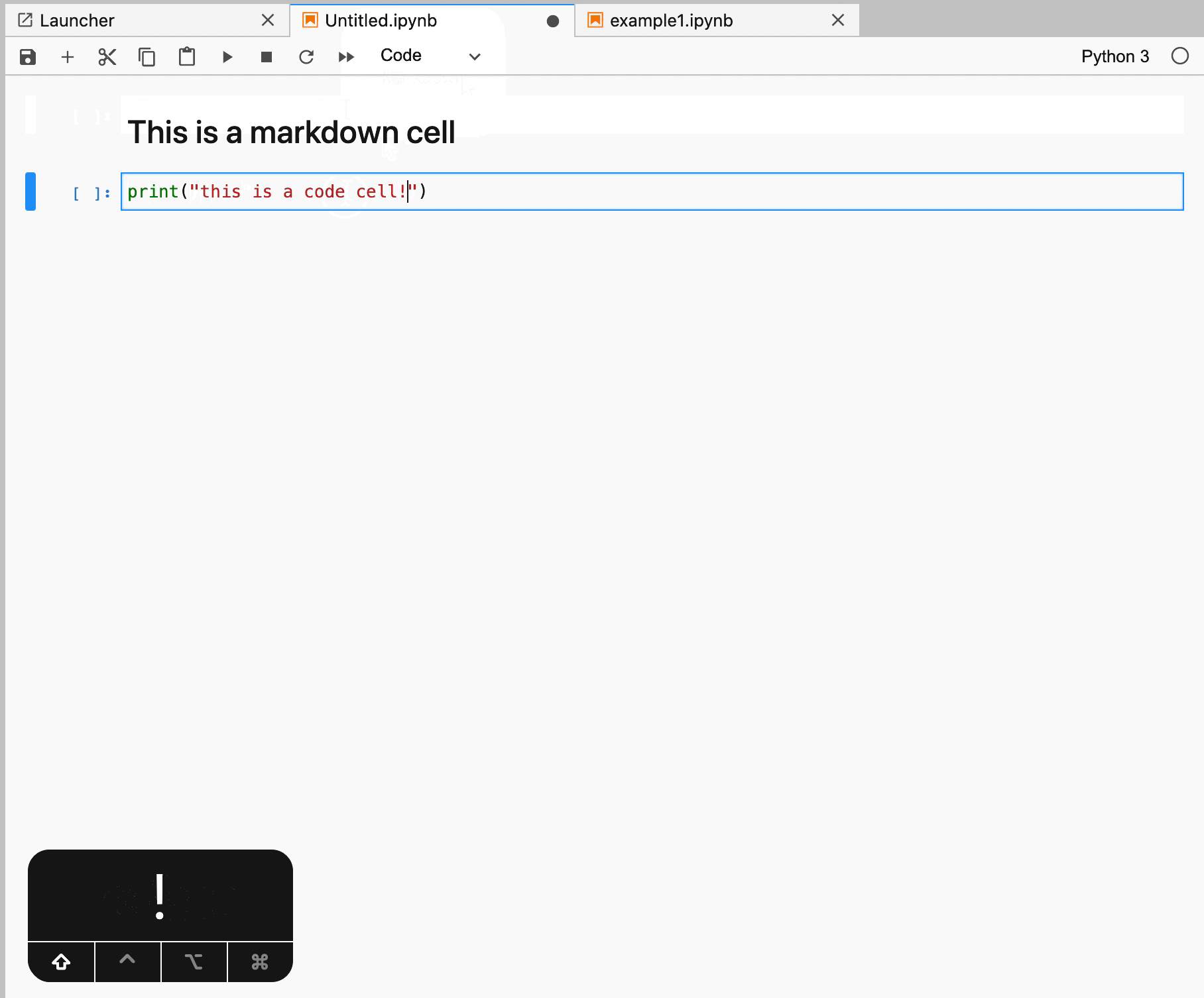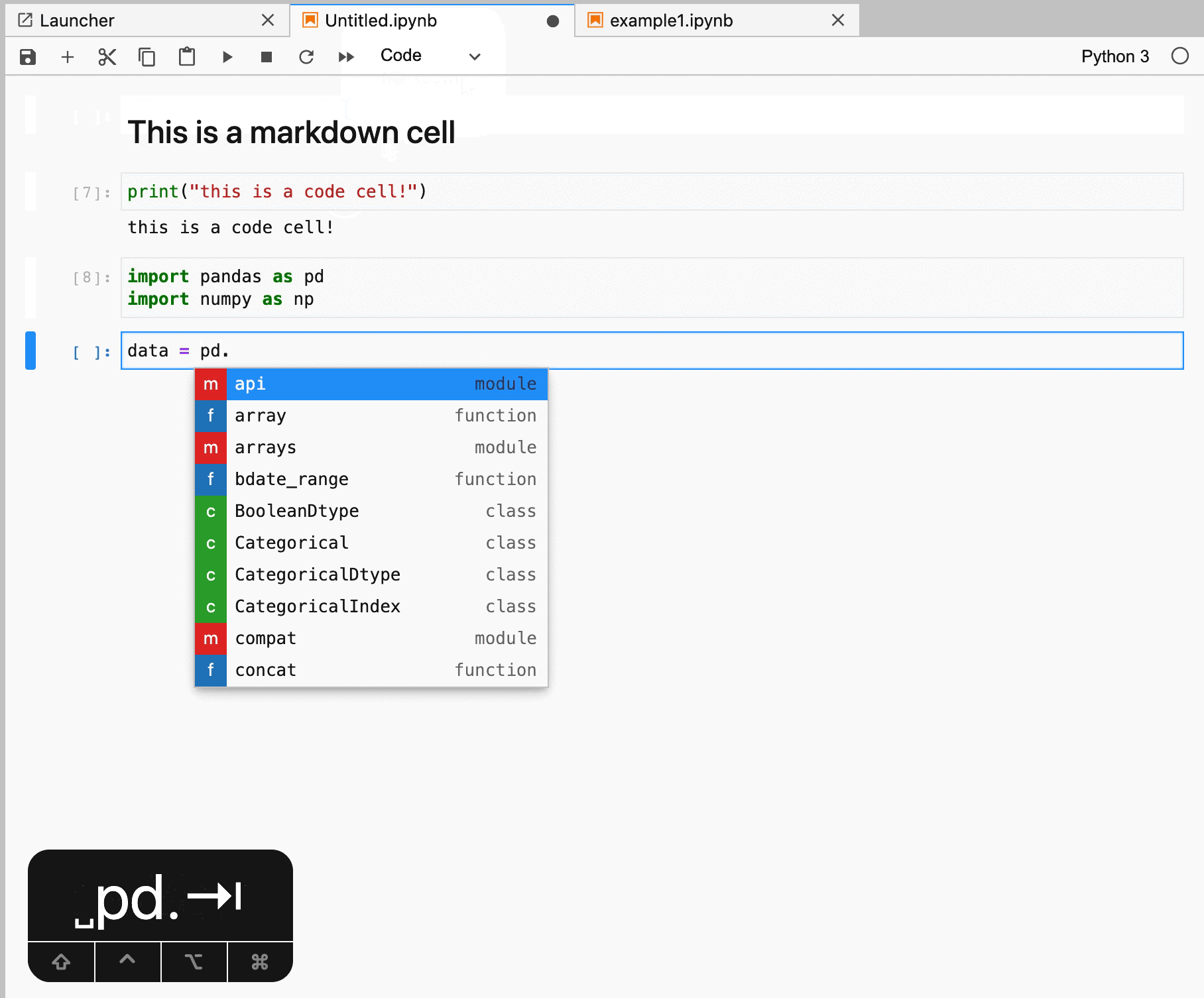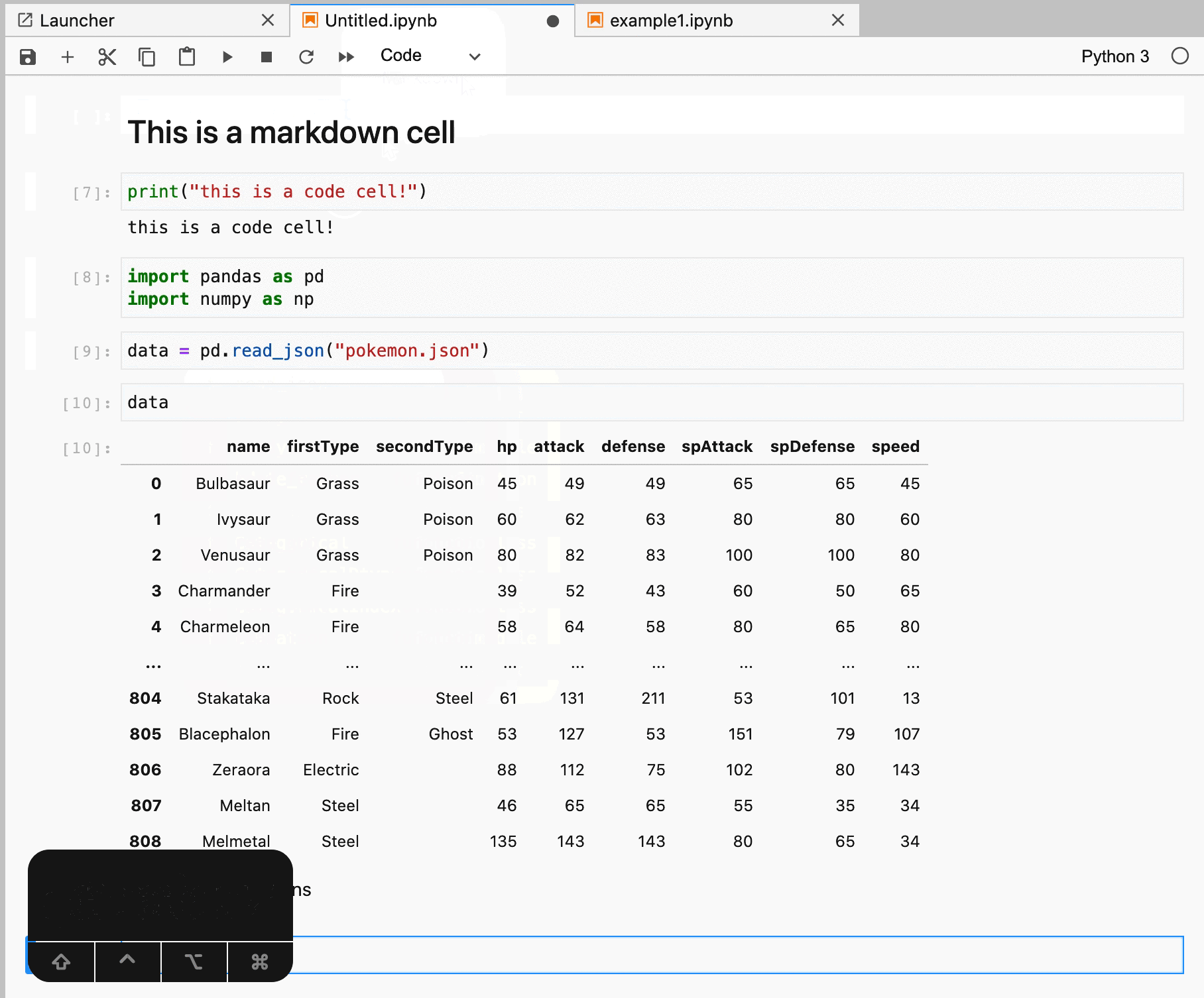
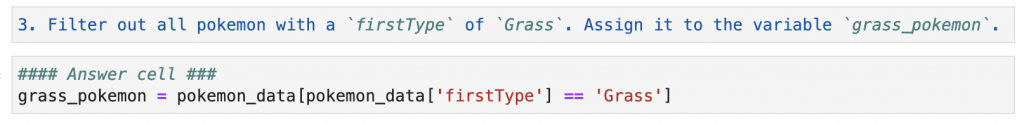
Using Jupyter Notebooks (with a combination of the matplotlib library) it becomes almost trivial to visualize large datasets
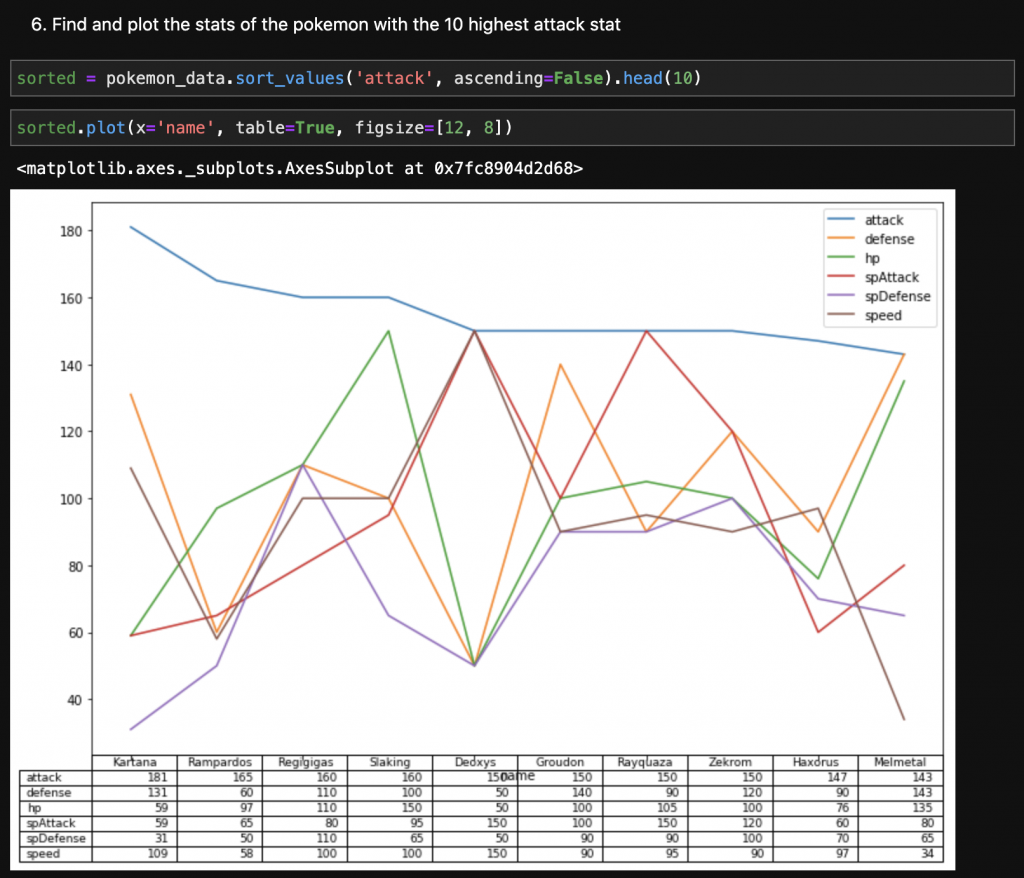
Jupyter Notebooks are a great option for instructors!
With Juptyer Notebooks, the instructor can release a version of the notebook with instructions written in markdown to their students. The students can then follow along interactively, or submit their notebooks for grading (via Moodle, git, etc).
An example notebook with instructions may look something like the following
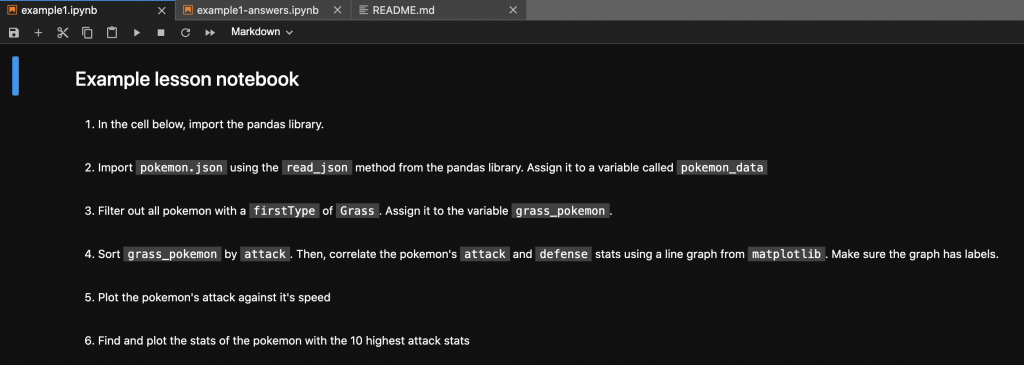
While a completed notebook may look like this
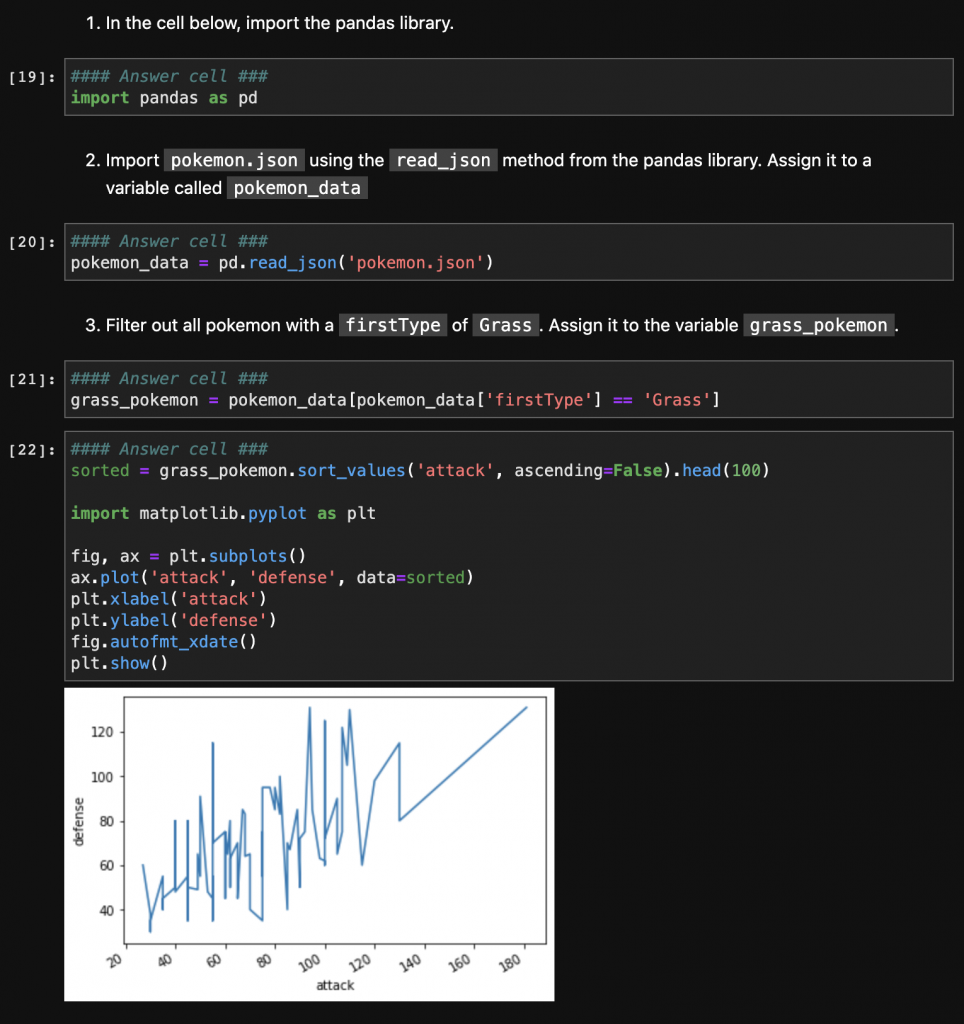
You can view the full example notebooks at https://github.com/Swarthmore/example-jupyter-notebooks or by clicking the following to access them directly
The following packages are available for use on all Swarthmore-hosted Jupyter notebooks
Jupyter Tips & Tricks
- You can use
shift + returnto run the current cell of your Notebook, and start a new one. - Pressing
tabwill invoke the notebook’s autocompletion feature - You can press
Esc00to quickly restart your notebook - Jupyter notebooks have a
commandand aneditmode. When your cursor is active inside a cell, you are ineditmode. You can switch tocommandmode by pressingEsc - In
editmode, pressCtrl + Shift + -to split the current cell - In
commandmode, pressShift + Mto merge the selected cells - In
commandmode, you can delete the current cell by typingdd - Jupyter notebooks run in GitHub!
More Reading
For access to Swarthmore’s hosted Jupyter notebooks, please contact the Swarthmore help desk

